Buy Stock Conical Tapered Compression Springs - 350 Designs
Buy Stock Conical Springs
Enter your Outer Diameter and Free Length
Hint: For larger search results, enter a bigger range of Min and Max Inputs
Enter your Outer Diameter and Length Inside Hook
Hint: For larger search results, enter a bigger range of Min and Max Inputs
Enter your Outer Diameter and Total Coils
Hint: For larger search results, enter a bigger range of Min and Max Inputs
Enter you Small Outer Diameter, Large Outer Diameter and Free Length
Hint: For larger search results, enter a bigger range of Min and Max Inputs
There are several material types available. Based on your application, you can select the best material to match your demands and environmental requirements. If your spring is enclosed in your device and doesn’t run the risk of being wet or exposed to temperatures higher than 250º Fahrenheit (121º Celsius), you can choose a high carbon spring wire. High carbons are not satisfactory for shock or impact loading. For these conditions, we recommend you use an alloy steel wire which is more resistant to conditions involving high stress. On the other side, if you need a corrosion-resistant coil spring, we can supply springs made of stainless steel. There are 3 main types of stainless steel and each of them offer different temperature limitations as well as hardness/elasticity. For more information on material types and their properties, click here.
Conical tapered compression springs are made from round spring tempered wire with a unique cone-shaped profile , featuring a body that tapers from a larger outer diameter at the base to a smaller outer diameter at the top. This structural arrangement not only boosts the spring's ability to absorb shocks, but also prevents the issues associated with bending or buckling that are common in traditional compression springs by giving it a larger outer diameter base, thus giving the conical compression spring more stable footing. Design benefits like a telescoping structure—in that the smaller diameter coils, when compressed, nestle inside the bigger diameter coils—permit the length of the conical spring to telescope down to practically one wire diameter of height. This is especially important in applications where vertical space is limited, but large compressive forces are needed, as the tapered shape allows the spring to compress into a compact form without loss of stability.
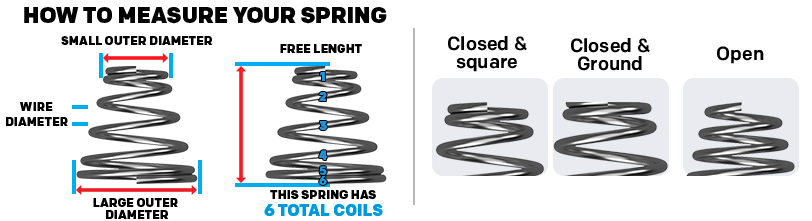
Measuring a conical tapered compression spring accurately is essential for ensuring that it fits properly into your application and functions as intended. Every dimension of the spring plays a crucial role in its performance, so it's important to take precise measurements. Here's an expanded guide to help you measure your conical tapered spring effectively, along with explanations of how each measurement affects the spring's design and application.
Before you start, gather the necessary tools: a set of dial or digital calipers.. This instrument will enable you to measure different aspects of the spring with precision , which is crucial for obtaining accurate data.
Measure the Outer Diameters:
-
Large Outer Diameter (Base Diameter):
- Use the calipers to measure the large outer diameter at the base of the spring. This diameter is the widest part of the spring and directly influences how the spring fits into its housing or assembly. A correct measurement ensures that the spring will not be too large or too small for its designated space, which is critical for proper function and stability.
-
Small Outer Diameter (Top Diameter):
- Next, measure the small outer diameter at the top of the spring. This is the narrowest part of the spring and affects how the spring interfaces with the components at the top of the assembly. The difference between the large and small outer diameters also dictates the taper angle, which can impact the spring’s load distribution and compression characteristics.
-
Effect on Design:
- The outer diameters determine the taper of the spring, which affects how the spring compresses and distributes force. A larger difference between the large and small diameters typically results in a more aggressive taper, which can influence the spring’s flexibility and load-bearing capacity.
Determine the Free Length:
-
Free Length Measurement:
- Place the conical spring in between the jaws of the caliper and slowly close the jaws of the caliper until the jaws barely touch both spring ends. Measure the tapered conical spring horizontally inside the jaws of the caliper from end to end. This is known as the free length of the conical spring, representing its length when fully extended and not under any load.
-
Measure the Wire Diameter:
-
Wire Diameter Measurement:
Use a dial or digital caliper to measure the wire diameter of the stock conical tapered compression spring. It’s important to take measurements at several points along the wire to ensure accuracy, as inconsistencies or variations in the wire diameter can affect the spring’s performance.
-
Wire Diameter Measurement:
-
Effect on Design:
- The wire diameter directly impacts the spring’s stiffness (spring rate) and its ability to bear load. Thicker wires result in a stiffer spring that can withstand higher loads, while thinner wires make the spring weaker but more flexible. This dimension is crucial for determining how the spring will respond to forces in its application.
Count the Total Coils:
-
Total Coil Count:
- Carefully count the total number of coils from top to bottom, including all visible coils. The total coil count is important for understanding the spring’s compressibility and solid height.
-
Effect on Design:
- The number of coils affects the spring’s rate of compression and its overall strength. More coils generally mean a softer spring with greater flexibility, while fewer coils result in a stiffer spring with a higher load capacity but less travel or deflection. The coil count also influences the spring’s solid height, which is the fully compressed length.

Check the Solid Height (if applicable):
-
Solid Height Measurement:
- Compress the conical spring until it can no longer be compressed further without causing damage. Measure the height of the compressed spring using a dial or digital caliper. This is known as the solid height or coil bind height, and it’s important for applications where space is limited.
-
Effect on Design:
- The solid height is critical for applications where the spring must fit into a confined space when fully compressed. It represents the minimum height the spring can achieve, which is essential for ensuring the spring does not interfere with other components when under maximum load.
Record Material Type and End Type (if required):
-
Material Type:
- Note the material of the spring (e.g., stainless steel, music wire). Different materials offer varying levels of corrosion resistance, strength, and flexibility, which can significantly affect the spring’s performance and longevity in different environments.
-
End Type:
- Identify the style of the ends (e.g., closed and squared, open ends). The end type affects how the spring interfaces with other components in the assembly and can influence load distribution and the spring’s overall function.
-
Effect on Design:
- The material type and end type are crucial for ensuring that the spring meets the operational demands of its application. Material selection affects durability and resistance to environmental factors, while the end type can impact how the spring is installed and how it interacts with other parts of the system.
Document All Measurements:
-
Accurate Record Keeping:
- Ensure all measurements are recorded accurately, and take multiple measurements of critical dimensions like wire diameter and outer diameters to verify consistency. This data is essential for selecting or designing a spring that will perform reliably in its intended application.
By carefully measuring and recording each of these dimensions, you gain a thorough understanding of the conical spring’s characteristics , ensuring that it will perform as expected in your specific application. Each measurement plays a crucial role in determining the spring’s fit, function, and durability, making accuracy essential for optimal spring performance.
Understanding End Types for Stock Conical Springs: Selecting the Right Configuration for Optimal Performance
When selecting conical springs for various applications, understanding the different end types available is crucial, as they significantly influence the spring's function and integration into mechanical assemblies. Here’s a more detailed look at each end type:
- Closed and Ground Ends: Closed and ground ends are achieved by bringing the end coils of the spring into complete closure, then grinding them down to create a flat and even surface. This process enhances the spring’s stability and allows for more even distribution of forces across the contact area when the spring is compressed. Such precision is particularly important in applications requiring high levels of accuracy and minimal variability in spring performance, such as in precision machinery and high-load bearing assemblies. The uniformity provided by this type of end also helps in reducing premature wear and tear.


- Closed and Squared Ends: In closed and squared ends, the ends are also brought into close but are not ground. Instead, they are squared off, aligning with the axis of the spring. This type ensures that the spring stands upright and operates without tilting, thereby providing stability similar to closed and ground ends but at a lower cost. This type of end is suitable for general applications where the precision of ground ends is not necessary, but where some level of end closure is beneficial for stability and performance.
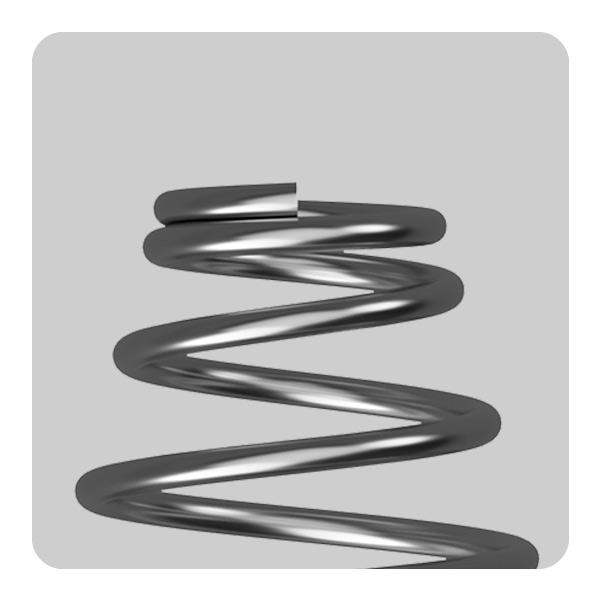


- Open Ends: Springs with open ends retain the natural shape of the coil and are not altered. This type provides the greatest flexibility and more load and is typically the most cost-effective option. Open-ended springs are easier to produce and thus more common in applications where the end configuration has minimal impact on the overall function of the spring. The only downside to open ends is that the conical springs will tangle very easily and must be packaged in small lots to prevent tangling. They are ideal for light to medium duty applications where the exact distribution of load is not critical.


Each end type is designed to meet specific functional and economic needs, making it important to consider factors such as operational environment, load requirements, and budget when choosing the appropriate end type for a conical spring. This choice will impact not only how well the spring fits into the assembly but also its longevity and effectiveness in the application. Understanding these options will allow designers and engineers to make informed decisions, optimizing the performance and cost-efficiency of their mechanical systems.
Selecting the Best Material and Finish for Stock Conical Springs: Ensuring Optimal Performance Across Applications
Our selection of stock conical tapered springs is designed to meet the diverse needs of various industries and applications. Whether you're seeking springs for general-purpose use, specialized environments, or specific mechanical functions, we have you covered with a wide range of options.
Material Choices:
We offer conical springs made from several high-quality materials, each chosen for its unique properties:
- Music Wire ASTM A 228: Ideal for general applications, Music Wire provides a reliable balance of strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It is well-suited for dynamic or high-stress environments where consistent performance is critical.
- Stainless Steel ASTM A 313: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, Stainless Steel is perfect for applications exposed to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive elements. It’s a go-to choice for medical, food processing, and outdoor equipment industries where longevity and resistance to rust are paramount.
- Hard Drawn ASTM A 227: For projects where budget considerations are key, Hard Drawn wire offers an economical solution without compromising on basic functionality. It is a practical choice for low-stress applications where environmental conditions are controlled.
- Oil Tempered ASTM A 229: This material is treated to enhance thermal resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature environments. It’s often used in applications that experience heat cycling or where thermal stability is a necessity, such as in automotive and industrial machinery.
- Phosphor Bronze ASTM B 159: Offering excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, Phosphor Bronze is ideal for applications in the electronics industry, such as in electrical connectors and springs that require reliable performance in humid or corrosive environments.
Finishing Options:
To further enhance the durability and performance of our springs, we offer a variety of finishing options tailored to your environmental and operational requirements:
- Zinc Plating: This finish provides an extra layer of corrosion protection, particularly useful in outdoor or humid environments, extending the lifespan of the spring.
- Black Oxide: For applications where appearance and corrosion resistance are important, Black Oxide offers a sleek, matte finish while protecting the spring from oxidization.
- Gold Iridite: This finish provides not only corrosion resistance but also a distinctive aesthetic appeal. It’s often used in high-visibility or decorative applications where both function and form are critical.
By offering a broad selection of materials, end types, and finishes, we ensure that you can find the perfect conical spring for your specific needs. Our commitment to customization means that whether you’re facing demanding mechanical requirements or unique environmental challenges, our springs are designed to deliver optimal performance and longevity.
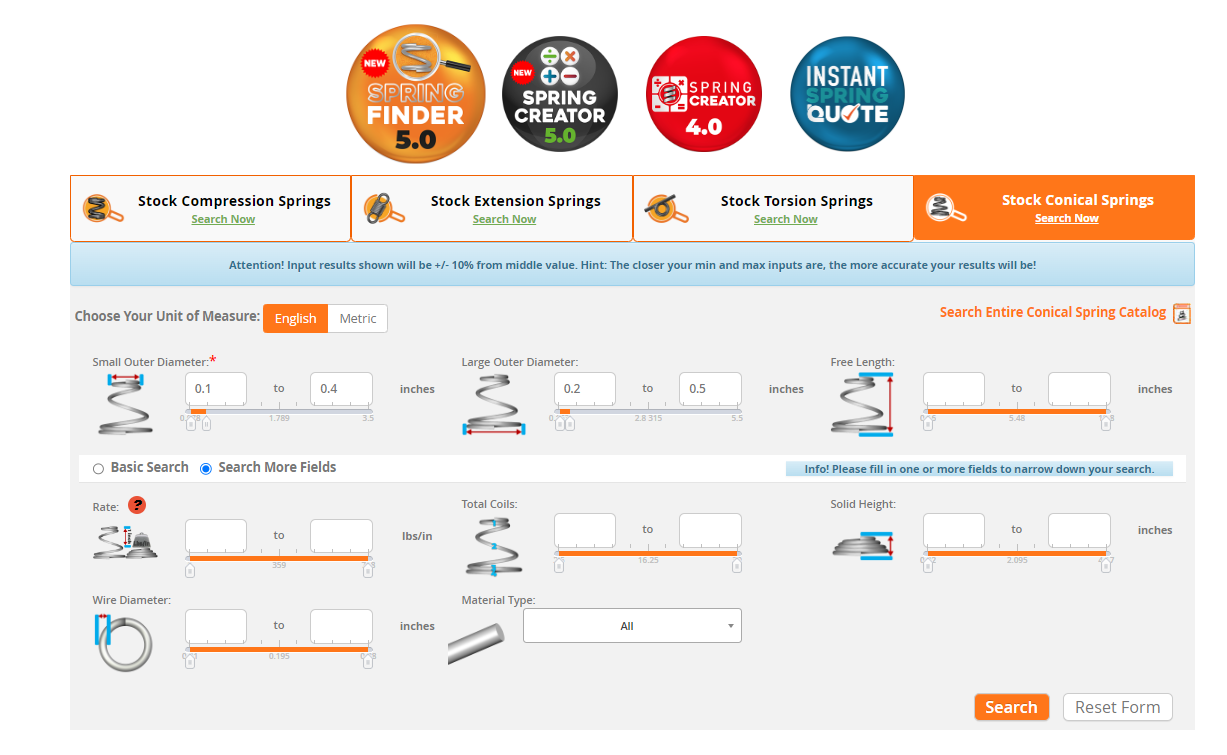
Finding the perfect conical spring for your application can be a challenging task, especially when considering the wide range of specifications and materials available. However, with Spring Finder 5.0, the process becomes streamlined and intuitive. This powerful tool is designed to help you quickly identify the conical spring that meets your exact requirements, saving you time and ensuring optimal performance in your application.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
The first step in using Spring Finder 5.0 is to clearly define your spring requirements. Start by entering the basic parameters, such as the outer diameter range, free length, and wire diameter. You can also specify the desired material type, whether you need Music Wire for general use, Stainless Steel for corrosion resistance, or another specialized material. Spring Finder 5.0 allows you to fine-tune these criteria to narrow down your options to the most suitable springs.

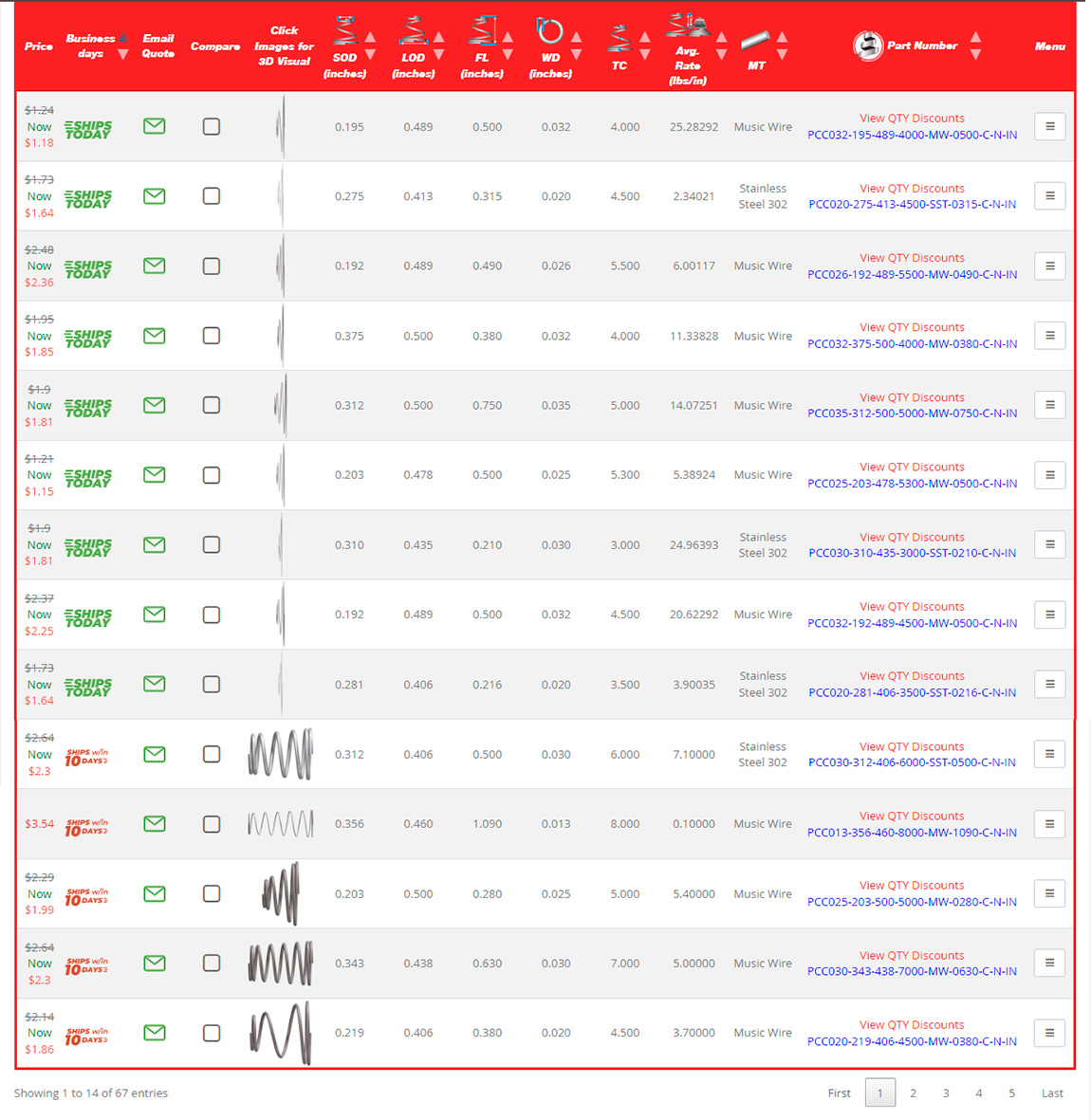
Step 2: Review the List of Options
Once you've entered your basic parameters, Spring Finder 5.0 will generate a list of potential tapered springs that match your criteria. At this stage, it’s important to carefully review the options provided. Examine the specifications of each spring to see how closely they align with your project’s needs. Look for critical factors such as total coils, material suitability, and dimensional accuracy. This review process helps you identify the springs that are most likely to perform well in your specific application.

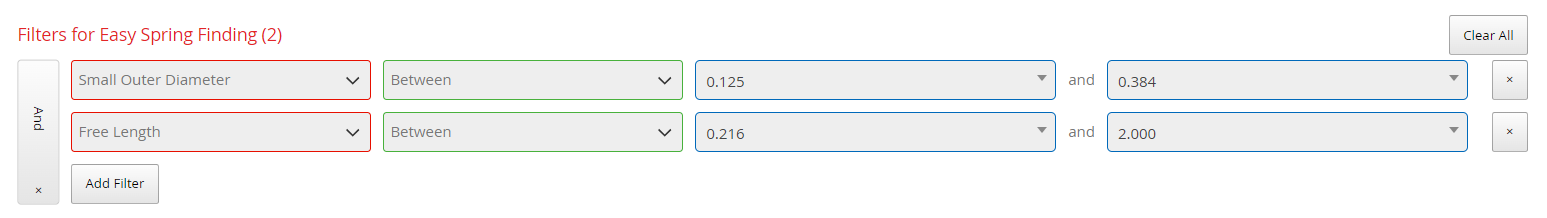
Step 3: Filter the Results
After reviewing the initial list of options, you can use the advanced filtering tools in Spring Finder 5.0 to further narrow down your selection. This step allows you to apply additional criteria, such as specific free length, wire diameter, or even more precise dimensional tolerances. By filtering the results, you can eliminate less suitable options and focus on springs that offer the best combination of performance characteristics and fit for your project. This refined list makes it easier to make an informed decision and ensures you select a spring that meets both your operational and environmental requirements.

Step 4: Download 3D CAD File and 3D Blueprint
Once you've identified the ideal spring for your application, Spring Finder 5.0 offers the option to download a 3D CAD file and a 3D blueprint of the selected spring. This feature is invaluable for engineers and designers who need to integrate the spring model into their design software or for those who require detailed visual references during the prototyping phase. By downloading these files, you can seamlessly incorporate the spring into your digital models, ensuring a perfect fit within your assembly and streamlining the design and production process.
By following these steps and leveraging the advanced features of Spring Finder 5.0, finding the right conical spring for your application becomes a straightforward and efficient process. Whether you're working on a prototype or selecting a spring for mass production, this tool ensures that you get the precise spring you need, tailored to your specific requirements.
When designing a conical spring , one important aspect to consider is the telescoping effect, which involves the way the coils overlap or nest inside one another during compression. The telescoping effect is influenced by several factors, including the diameters of the coils, the pitch (the distance between coils), and the material properties of the spring.
We'll be using the conical spring with the part number PCC080-750-2187-10000-SST-2500-CG-N-IN as our reference to illustrate how to calculate the telescoping capabilities of a conical spring. This spring features a Small Outer Diameter of 0.750 inches, a Large Outer Diameter of 2.187 inches, 10 total coils, and a Wire Diameter of 0.080 inches. By sticking with these specific dimensions, we can keep things clear and consistent as we dive into this essential concept and its practical application.
This particular conical spring is designed to nest within itself when compressed, making it an ideal candidate for scenarios where space efficiency is crucial. We'll explore how these parameters influence the spring's ability to telescope and calculate the resulting solid height when fully compressed. Understanding this concept will help us appreciate the design nuances that make conical springs versatile and effective in various mechanical applications.
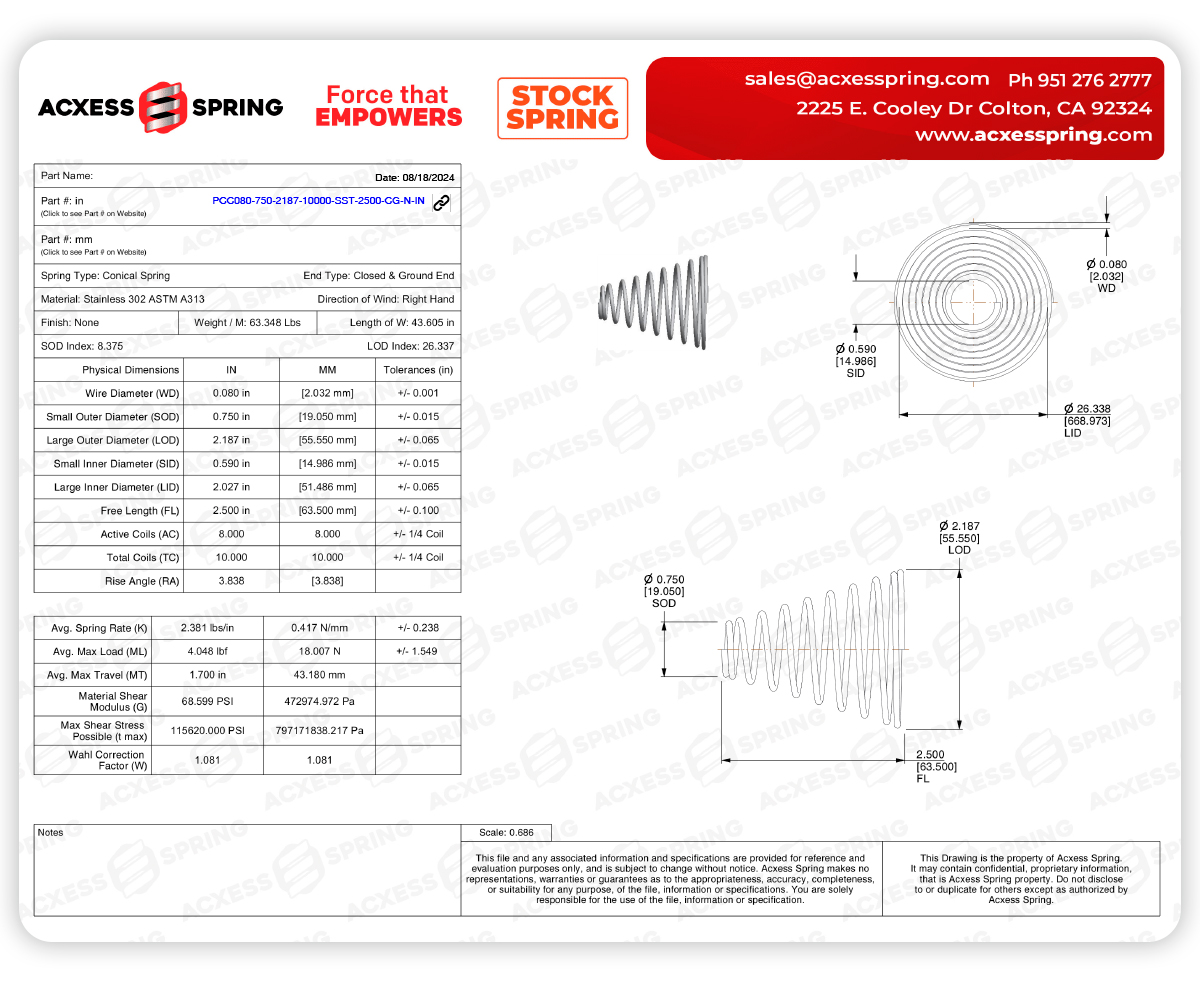

|
Part Number |
PCC080-750-2187-10000-SST-2500-CG-N-IN |
|
Small Outer Diameter (SOD) |
0.750 inches |
|
Large Outer Diameter (LOD) |
2.187 inches |
|
Total Coils (TC) |
10 |
|
Wire Diameter (WD) |
0.080 inches |
Step 1: Check the Telescoping Condition
For telescoping to occur, starting from the small outer diameter each subsequent coil diameter should be larger than the previous coil by at least the wire diameter, WD.
Given that we have 10 total coils (TC) which is 8 active coils (AC), the space for the smaller outer diameters to nestle is calculated as follows.
2.187 (LOD) - 0.750 (SOD) = 1.437 Space to Nestle or Telescope
Then the increment per coil can be calculated as:
Increment per coil = WD × 2 = 0.160
1.437 / 0.160 = 8.98 active coils space
This Conical Tapered Compression Spring WILL Telescope or Nest inside itself.
Step 2: Calculate Solid Height without telescoping
The Solid Height (SH) for the spring is calculated by:
SH = TC × WD + 1WD =
10 × 0.080 + 1 WD = 0.880 inches
This indicates that when fully compressed, the solid height of the spring is approximately 0.880 inches.
Step 3: Practical Considerations
For telescoping to work perfectly:
- The increment between each coil must consistently be greater than the wire diameter, which in this case it is (0.16 inches > 0.080 inches).
- Spring Design: Since the end type is "Closed & Ground," the last coil will have reduced active deflection, and the spring may not fully telescope if it’s close-wound at the ends.
Based on the provided dimensions and calculations, the conical spring should be capable of telescoping without the coils binding, allowing it to achieve a solid height of approximately 0.080 inches. This design also ensures that the spring will compress effectively, making it suitable for applications where space efficiency is critical.

To help in the evaluation and selection of the right springs for your applications, we encourage users to visit our website and download our full stock conical springs catalog in PDF format . This catalog is designed to provide an extensive overview of our products, including detailed specifications and potential applications, helping users make well-informed decisions on spring selection based on their specific project requirements.
To deepen your understanding of conical springs and ensure you make the most informed decisions for your projects, we highly recommend exploring Acxess Spring's Knowledge Base . This comprehensive resource offers detailed insights, guides, and expert advice on everything related to conical springs. Explore the wealth of information at Acxess Spring and empower yourself with the knowledge to make well-informed decisions on all your spring-related projects. Start learning today and see the difference expert insights can make!
Ready to Find the Perfect Conical Spring for Your Project? Use Spring Finder 5.0 to Streamline Your Search and Get the Ideal Fit Today!
Understanding how to measure and choose the correct spring dimensions can be challenging, but with Spring Finder 5.0, the process is simplified. This intuitive tool allows you to input your specific requirements and quickly narrow down the best options from a wide selection. Don’t leave your spring selection to chance—use Spring Finder 5.0 today to find the perfect conical spring tailored to your exact needs!













