Spring Rate Calculator
Attention! Input results shown will be +/- 10% from middle value. Hint: The closer your min and max inputs are, the more accurate your results will be!
Attention! Input results shown will be +/- 10% from middle value. Hint: The closer your min and max inputs are, the more accurate your results will be!
Attention! Input results shown will be +/- 10% from middle value. Hint: The closer your min and max inputs are, the more accurate your results will be!
Definition: Spring rate, also known as spring constant, is the constant amount of force or spring rate of force it takes an extension or compression spring to travel an inch of distance or, in the metric system of measurement, a millimeter of distance. The units of measurement of rate in the English System are, lbf/in (pounds of force per inch) or N/mm (newtons per millimeter) in the Metric System.
Spring rate is the most important part of your compression or extension spring design, but it is also the most complicated spring calculation. You have to take every one of your spring's physical dimensions into account including the material type. Below, you are provided with our free online spring calculator, "Spring Creator", to make your spring calculations a lot easier and faster.
The calculation of spring rate is linear on extension and compression springs; unlike torsion springs where the force is radial. Knowing your spring rate will determine if your spring will function correctly under your working loads. The formulas shown below will explain just how to calculate your compression and extension spring rate.
Formula to Calculate Rate:
- D = D outer - d<
- G = E ÷ 2 ( 1 + V)
- k = Gd^4 ÷ (8D^3 na)
Formula to Calculate Rate Acquired From Hooke's Law:
- k = F ÷ x
Formula Symbols:
- d = Wire Diameter
- D outer = Outer Diameter
- D = Mean Diameter
- E = Young's Modulus of Material
- G = Shear Modulus of Material
- L free = Free Length
- k = Spring Rate (Spring Constant)
- na = Active Coils
- v = Poison's Ratio of Material
Formula Symbols:
- k = Spring Rate (Spring Constant)
- F = Force
- x = Distance Traveled

Attention! Input results shown will be +/- 10% from middle value. Hint: The closer your min and max inputs are, the more accurate your results will be!
Attention! Input results shown will be +/- 10% from middle value. Hint: The closer your min and max inputs are, the more accurate your results will be!
Attention! Input results shown will be +/- 10% from middle value. Hint: The closer your min and max inputs are, the more accurate your results will be!
What Is Spring Rate?
Spring rate, commonly referred to as the spring constant (k), is essentially the stiffness of a spring. It quantifies the amount of force required to compress or extend a spring by a unit of distance like lbs per inch or newtons per millimeter. In other words, it answers the question: "How much force do I need to apply to make this spring move a certain distance?"
Understanding spring rate is crucial because it determines how a spring will react under different loads. A high spring rate means the spring is stiff—it takes more force to compress or extend it. A low spring rate indicates a more flexible spring that requires less force to achieve the same deflection or travel.


Why Is Spring Rate Important in Design?
Imagine designing a trampoline with springs that are too stiff: you'd feel like you're jumping on solid ground. On the flip side, if the springs are too soft in a car suspension, every bump would turn your drive into a rollercoaster ride. Here's why getting the spring rate right is a big deal:
- Functionality: Ensures the spring performs its intended function, whether absorbing shocks or returning to its original position after compression.
- Safety: Prevents mechanical failures that could lead to accidents or equipment damage.
- Performance: Optimizes how a product behaves under load, enhancing user experience.
- Cost-Efficiency: Helps in selecting the right materials and dimensions, saving on manufacturing costs.
By accurately calculating and selecting the appropriate spring rate, designers and engineers can tailor springs to meet specific requirements, ensuring that products are both effective and reliable.
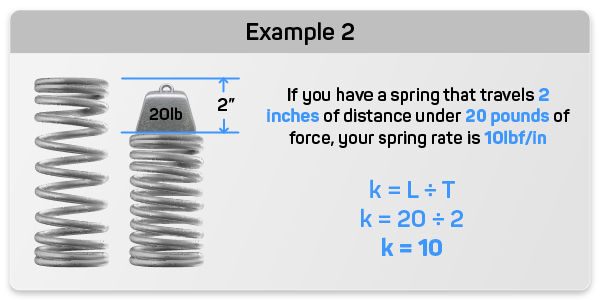

Fundamental Formulas for Calculating Spring Rate
Calculating spring rate isn't as daunting as it might seem. It involves a few fundamental formulas that consider the spring's physical dimensions and the material's properties. Let's break them down step by step.
Mean Diameter Calculation
First up is finding the mean diameter (D) of the spring, which is crucial for the next calculations.
D = OD − d
- D: Mean Diameter
- OD: Outer Diameter of the spring
- d: Wire Diameter
The mean diameter is essentially the average diameter around which the spring coils are wound. It affects how the spring will compress or extend under a load.
Shear Modulus of Material
Next, we need the shear modulus (G) of the material, which measures the material's rigidity.
G = E ÷ 2 ( 1 + V)
- G: Shear Modulus
- E: Young's Modulus of the material
- v: Poisson's Ratio of the material
The shear modulus depends on the material type (e.g., steel, stainless steel, bronze) and impacts how the material deforms under shear stress.
Spring Rate Formula
Now, we can calculate the spring rate (k) using the following formula:
k = Gd^4 ÷ (8D^3 * n)
- k: Spring Rate
- G: Shear Modulus
- d: Wire Diameter
- D: Mean Diameter
- n: Number of Active Coils
This formula tells us how the spring's physical dimensions and material properties combine to determine its stiffness.
Hooke's Law Application
For a more general approach, especially when dealing with experimental data, Hooke's Law comes into play:
k = F ÷ x
- k: Spring Rate (Spring Constant)
- F: Force applied to the spring
- x: Distance the spring travels (compression or extension)
This formula is particularly useful when you have the force and displacement data and want to find the spring rate experimentally.
Practical Example
Let's put these formulas to work:
Example 1: Calculating Spring Rate for a Compression Spring
Scenario: You're designing a compression spring for a mechanical device and need to calculate its spring rate. In this case, we’ll use Acxess Spring's Stock Part Number PC072-750-7500-SST-1750-C-N-IN for the example:




From the blueprint, we know:
- Wire Diameter (d): 0.072 inches
- Outer Diameter (OD): 0.75 inches
- Number of Active Coils (n): 5.5
- Material: Stainless Steel 302 ASTM A313 with a Shear Modulus (G) of 9949475.938 PSI
Step 1: Calculate Mean Diameter (D)
D = OD − d = 0.75 inches − 0.072 inches = 0.678 inches
Step 2: Calculate Spring Rate (k)
k = Gd^4 ÷ (8D^3 * n)
Plug in the numbers:
k = 9949475.938 PSI × (0.072 inches)^4 ÷ 8 × (0.678 inches)^3 × 5.5
Simplify:
d^4 = (0.072 inches)^4 = 0.000026873856
D^3 = (0.678 inches)^3 = 0.311665752
Now calculate:
k = 9949475.938 PSI × 0.000026873856 ÷ 8 × 0.311665752 × 5.5
k = 267.3807836332769 ÷ 13.713293088
k ≈ 19.49792671369738 lbs/in
Result:
The spring rate is approximately 19.498 lbs/in. This means it takes 19.498 lbs/in to compress the spring by one millimeter.
Using Online Tools for Spring Rate Calculation


Let's face it, manual calculations can be a headache, especially when you're dealing with complex designs or tight deadlines. That's where online tools like Acxess Spring's Online Spring Force Tester come into play, making the whole process as easy as pie.
Benefits of Using Online Tools
- Accuracy: Minimizes human error in calculations.
- Speed: Instant results save you valuable time.
- User-Friendly: Intuitive interfaces that don't require a Ph.D. in engineering.
- Additional Insights: Some tools provide stress analysis and material recommendations.
How to Use Acxess Spring's Online Spring Force Tester
Let's use Stock Part Number PC072-750-7500-SST-1750-C-N-IN to validate our previous calculations.
- Visit the Website: Go to Acxess Spring's Product View and navigate to Spring Creator and enter your spring dimensions, then click on the Online Spring Force Tester tab.
- Add Load: Provide a load that is within the Maximum Load limits, or specify a Loaded Height. The missing value will be automatically calculated when you press the tab key.
- Review Results: The tool will display the spring rate and other relevant data.
- Adjust as Needed: You can go back and tweak the parameters to see how changes affect the spring rate.




Pro Tip: Use the tool to experiment with different materials or dimensions to optimize your spring design.
Factors Affecting Spring Rate
Understanding what influences spring rate helps you make smarter design choices. Let's delve into the key factors.


Material Type
The material you choose isn't just about cost or availability; it significantly impacts the spring's performance.
- Young's Modulus (E): Indicates the stiffness of the material.
- Poisson's Ratio (v): Describes how the material deforms in directions perpendicular to the applied force.
Common Materials:
- Music Wire: High strength, ideal for dynamic loads.
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, good for harsh environments.
- Phosphor Bronze: Excellent for electrical applications due to conductivity.
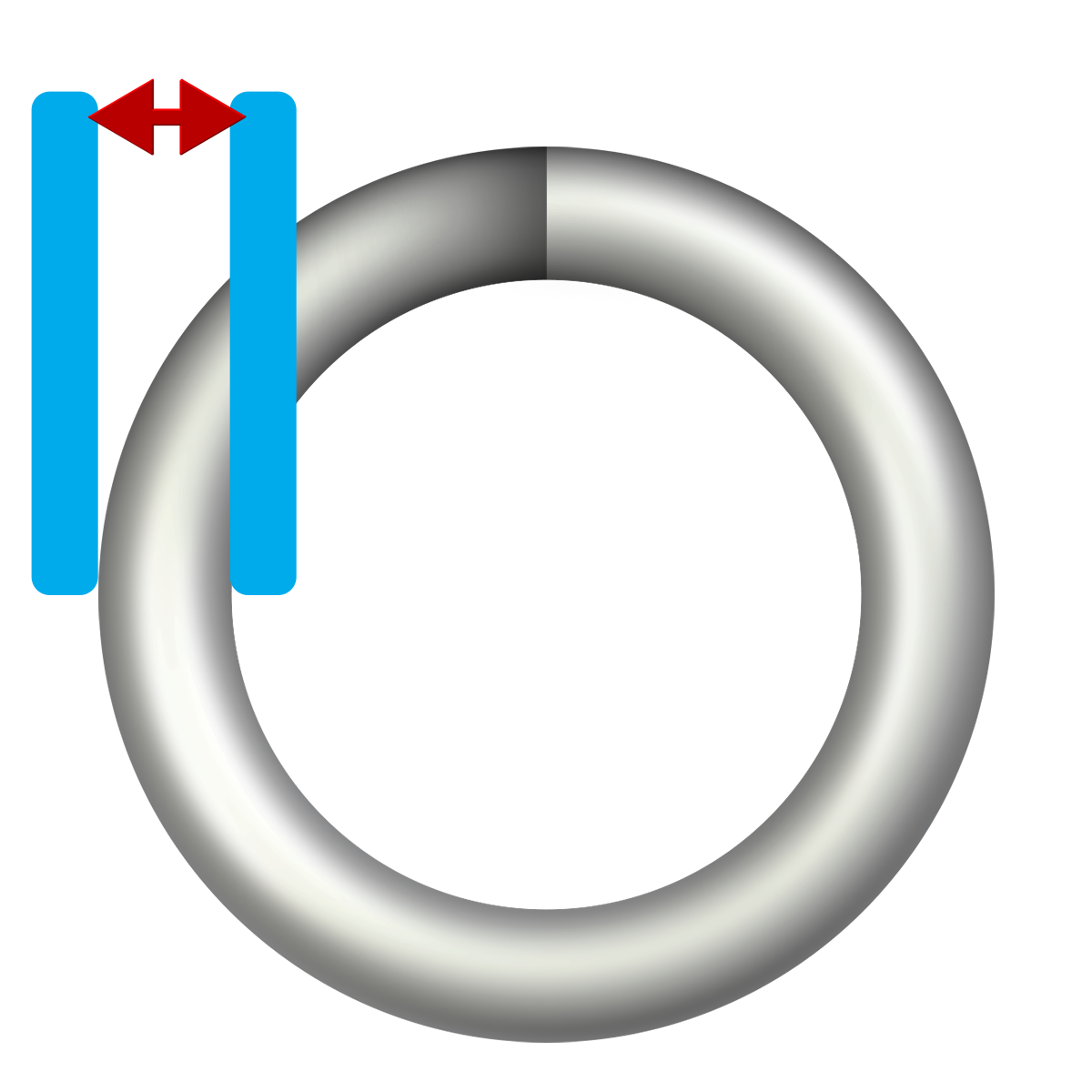

Wire Diameter
Since wire diameter (d) is raised to the fourth power in the spring rate formula, even minor changes can have a big impact.
- Thicker Wire: Increases spring rate (stiffer spring).
- Thinner Wire: Decreases spring rate (weaker spring).
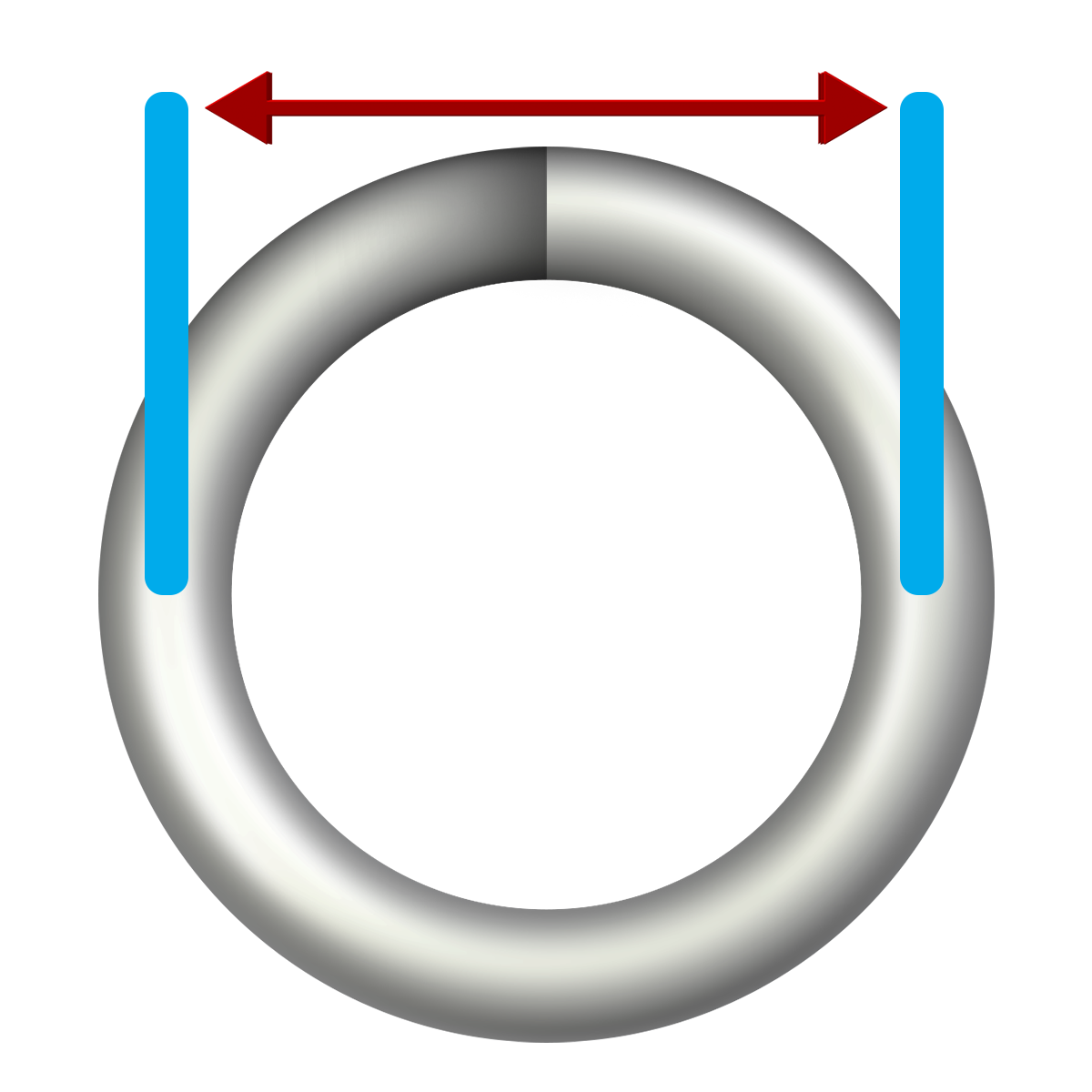

Coil Diameter and Number of Active Coils
- Mean Diameter (D): A larger mean diameter decreases the spring rate, making the spring less stiff.
- Number of Active Coils (n):
- More Coils: Lower spring rate (softer spring with more travel).
- Fewer Coils: Higher spring rate (stiffer spring with less travel).
Design Tip: Balancing all these factors allows you to fine-tune the spring's characteristics to meet specific requirements.
How to Find Spring Constant Calculator?
Calculating spring rate might seem like cracking a complex code, but once you understand the fundamentals, it's pretty straightforward. To simplify the process and enhance accuracy, consider using online tools designed for spring calculations. One such resource is Acxess Spring's Online Spring Force Tester, which allows you to input specific parameters and receive immediate feedback on spring performance. Additionally, Spring Creator 5.0 is a comprehensive tool that enables you to design custom springs tailored to your exact specifications.
By leveraging these tools, you can efficiently calculate and adjust spring rates to meet your project's needs. Whether you're designing a new mechanism or refining an existing one, understanding and applying these principles will help ensure your springs function as intended.
Five Key Takeaways
- Spring Rate Defines Stiffness: It's the force required per unit of displacement, crucial for predicting spring behavior.
- Material Matters: Different spring materials have unique properties affecting the spring rate; choose wisely based on your application.
- Dimensions Are Critical: Wire diameter, mean diameter, and the number of active coils significantly influence the spring rate. Make sure the spring fits in your application and has play to work freely without binding in the environment it used.
- Use Online Tools: Save time and increase accuracy by utilizing tools like Acxess Spring's Online Spring Force Tester.
- Balance is Key: Adjusting one parameter affects others; find the right combination for optimal performance.
By keeping these points in mind, you're well on your way to mastering spring rate calculations and designing springs that do exactly what you need them to do.
Enhance your projects with Spring Creator 5.0
Precision is crucial in spring design, and with Spring Creator 5.0, you can achieve it with ease. Our tool allows you to design different types of springs and offers advanced features such as instant quotes and real-time simulations with the Online Spring Force Tester. Register now and access all the benefits of our platform. Create the perfect spring and take your projects to the next level!
Created by Alfonso Jaramillo Jr
President Acxess Spring
Over 40 Years of Experience in Spring Engineering and Manufacturing











